

Fragaria vesca Mignonette - alpine strawberry seeds


Fragaria vesca Mignonette - alpine strawberry seeds


Fragaria vesca Mignonette - alpine strawberry seeds


Fragaria vesca Mignonette - alpine strawberry seeds
Fragaria vesca Mignonette - alpine strawberry seeds
Fragaria vesca Mignonette
Wild Strawberry, Woodland Strawberry, Alpine Strawberry, European Strawberry
This item cannot be shipped to the selected country
Dispatch by letter from €3.90
More information
Schedule delivery date,
and select date in basket
This plant carries a 6 months recovery warranty
More information
We guarantee the quality of our plants for a full growing cycle, and will replace at our expense any plant that fails to recover under normal climatic and planting conditions.
Seed-only orders are dispatched by sealed envelope. The delivery charge for seed-only orders is €3.90.
Description
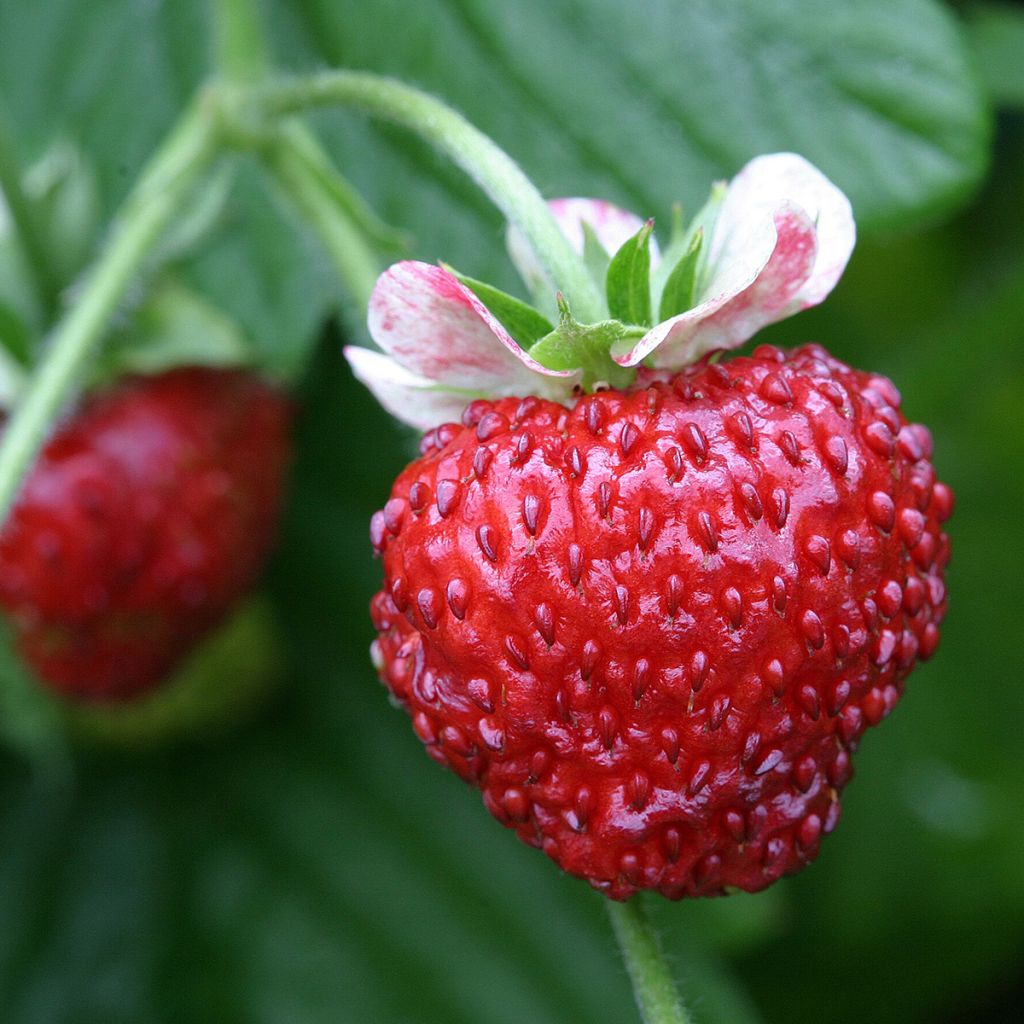
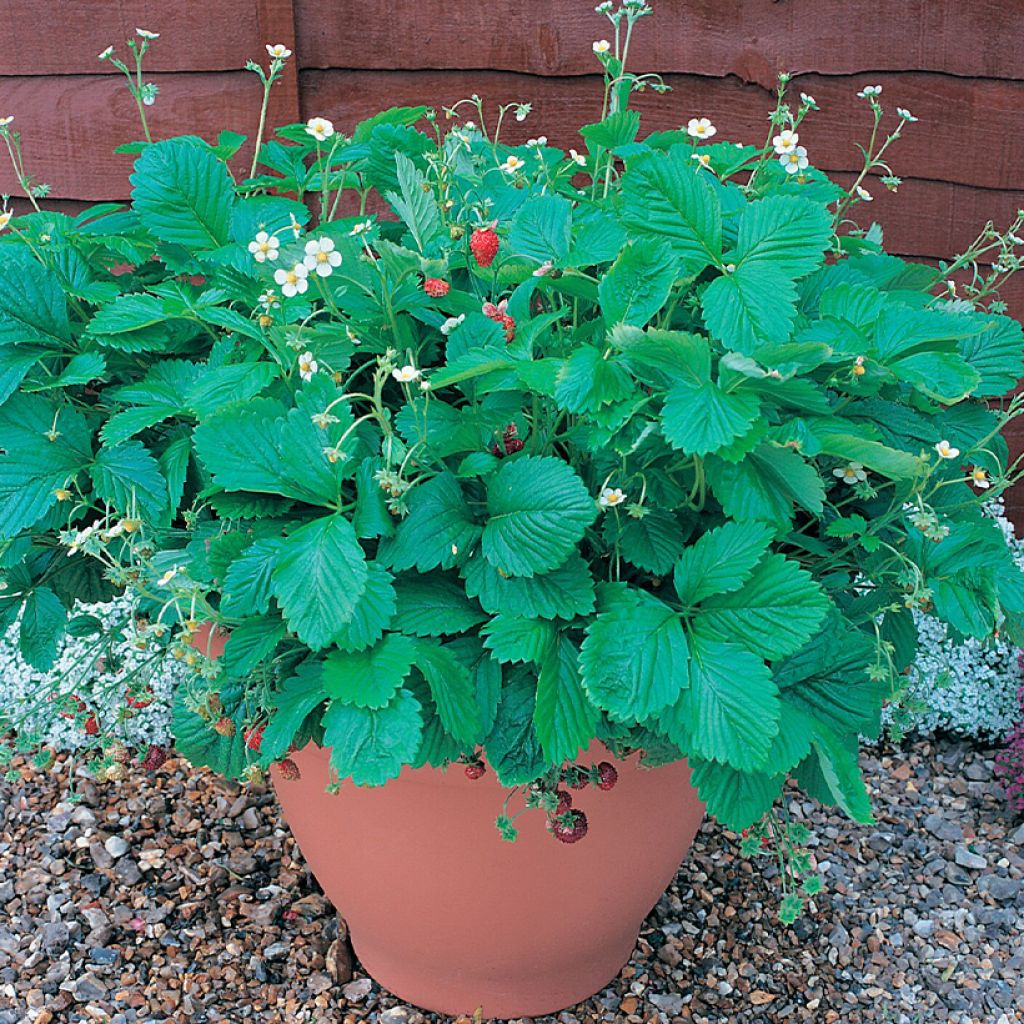
The Alpine Strawberry Mignonette is a variety that produces an abundance of 3 to 5 cm, shiny dark red fruits, larger than the typical species, with a regular shape and size and the same famous delicious and aromatic flavour. This 4-season strawberry is perpetual, allowing for multiple successive harvests. It is also very hardy. It is well-suited for cultivation in pots, planters, or hanging baskets. Sow from January to late April for a harvest from spring to late summer.
The strawberry is a perennial plant belonging to the Rosaceae family. Known throughout Europe since ancient times, it naturally grows in all the undergrowth of temperate regions. However, most of the juicy strawberries cultivated in our gardens are hybrids derived from a species native to Chile and brought back by the navigator Amédé François Frézier. There are several species of strawberries, the main ones being: Fragaria vesca or Alpine Strawberry, known for producing particularly fragrant small fruits, Fragaria moschata or Musk Strawberry, Fragaria viridis or Green Strawberry, the Valley Strawberry, which is less interesting due to the acidity of its fruits, and finally Fragaria chiloensis or Chilean Strawberry. These are wild strawberries. The cultivated strawberries with large fruits are almost all derived from the species Fragaria x Ananassa, which comes from Fragaria chiloensis and Fragaria Virginiana, another American species.
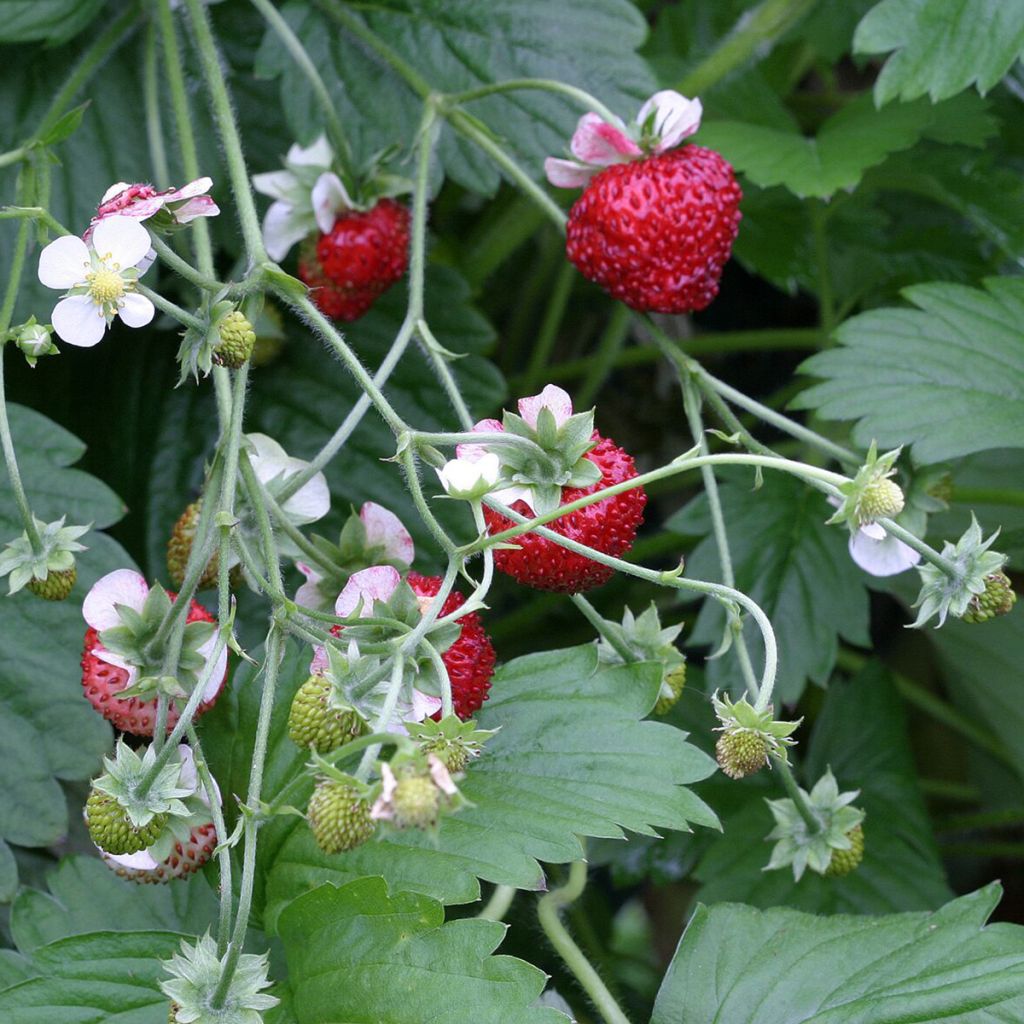
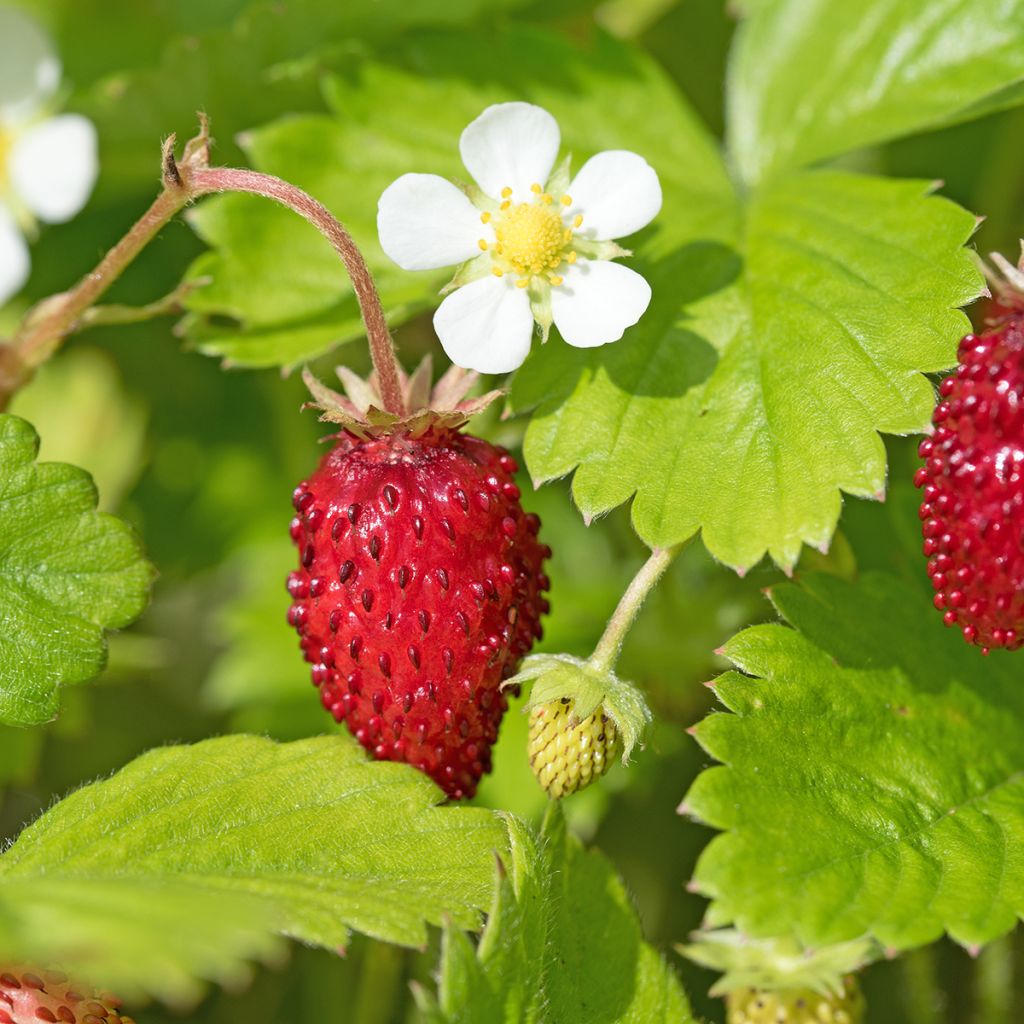
The strawberry has a spreading habit that can reach 40 cm in width and height. The evergreen leaves are trifoliate, obovate, well-toothed, and form dark green rosettes. Its flowering is characterised by a multitude of small white, yellow, or pink flowers with a golden centre. Then, depending on the varieties, they produce mostly red fruits, but some recent cultivars offer pink, yellow, or white strawberries. From a botanical point of view, strawberries are considered pseudocarps, with the achenes (seeds) appearing on the surface under the epidermis.
The flavour of the strawberry is very delicate and is characterised by a sweet and fruity aroma, sometimes with a slightly acidic note in the background. There are non-perpetual varieties that flower only once a year in spring and perpetual varieties that flower twice a year, or even continuously from spring to autumn. Strawberries are a (pseudocarp) fruit rich in vitamins B8 and B9, very rich in vitamins C and E, and provitamin A. They are remineralising, hypotensive, and purifying. It should be noted that they can cause a rash for some people, as they stimulate the release of histamine in the body.
Harvesting: pick the fruits as they ripen on the plants. Strawberries are delicate, so pick them with their stem by pinching 1 to 2 cm above the fruit. The texture of the fruit is a good indicator of its ripeness. It should be firm and slightly soft to the touch.
Storage: strawberries are best eaten fresh, simply with cream or as a topping for tarts. They can be stored for about a week in the vegetable drawer of your refrigerator. When they have been bruised or scratched, they will not keep as long. If you have a large harvest, remember that strawberries are fragile fruits. For longer preservation, consider using sugar, the best friend of fruits. You can make jams, marmalades, compotes, or syrups. You can also make ice cream or sorbets, but they will not keep as long. You can dry them in the oven after slicing them thinly to around 1 mm, you can then add them to your muesli. Finally, strawberries freeze very well. Small containers for freezing small fruits like strawberries, raspberries, or currants, etc., are now available.
Gardener's tip: strawberry plants are good companions for garlic, beans, lettuce, onions, leeks, thyme, and spinach. However, they do not like the company of cabbage and other brassicas.
Report an error about the product description
Harvest
Plant habit
Foliage
Botanical data
Fragaria
vesca
Mignonette
Rosaceae
Wild Strawberry, Woodland Strawberry, Alpine Strawberry, European Strawberry
Cultivar or hybrid
Perennial
Other Strawberry seeds
Planting and care
The strawberry plant is admired for its hardiness and simplicity of cultivation. It thrives in all types of soil, adapts to partial shade but prefers full sun while tolerating short periods of drought. As it readily multiplies through stolons, be careful not to let it spread too much.
Before sowing, you can place your seeds in the freezer compartment of your refrigerator for a few days, then in the vegetable drawer. This will aid germination after a period that can be compared to winter and the gradual warming of spring.
Sowing under a frame: sow from February to May in a warm place (16 to 18°C) in a tray with one-third seed compost, one-third garden soil, and one-third sand. Sow the seeds under a layer of compost 1 to 2 mm thick, then lightly press down. Water and make sure to keep the substrate moist. Strawberry plants take quite a while to emerge. You need to be patient and after about 35 days, the first seedlings will appear. When the plants have 5 to 6 leaves, transplant them into pots where they can continue to grow until they are planted in the ground.
Planting in the ground: once the risk of frost has passed, usually in mid-May, and when your plants have several leaves, transplant them into the ground. Dig a hole in the soil. If you plant multiple plants, space them 35 cm apart in all directions. Depending on the variety, you may have to wait before the first fruit.
Maintenance: regularly weed. It is beneficial to mulch your strawberry plants to maintain moisture and also to prevent the fruits from coming into contact with the ground, thus protecting them from grey rot.
Seedlings
Care
Intended location
This item has not been reviewed yet - be the first to leave a review about it.
Vegetable seeds
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Hardiness is the lowest winter temperature a plant can endure without suffering serious damage or even dying. However, hardiness is affected by location (a sheltered area, such as a patio), protection (winter cover) and soil type (hardiness is improved by well-drained soil).
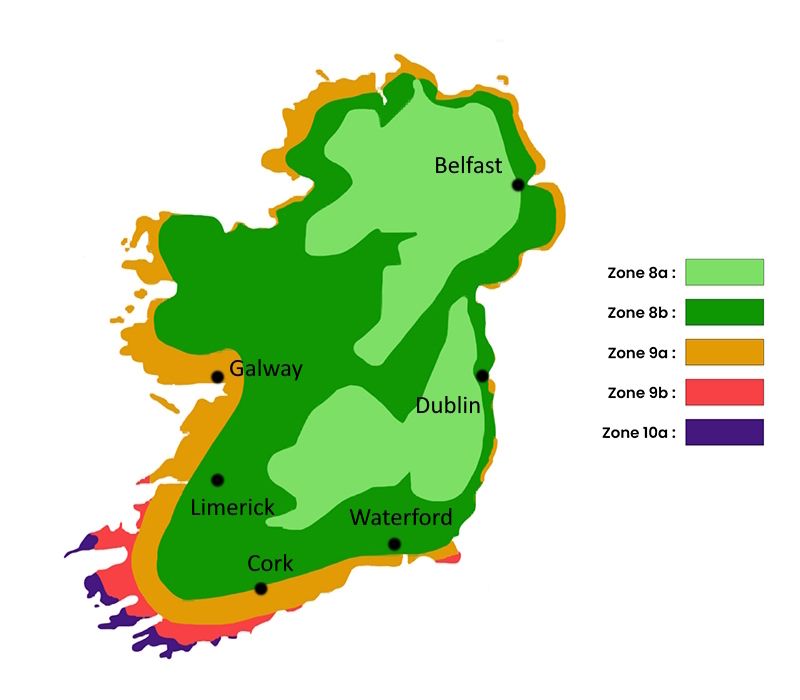
Photo Sharing Terms & Conditions
In order to encourage gardeners to interact and share their experiences, Promesse de fleurs offers various media enabling content to be uploaded onto its Site - in particular via the ‘Photo sharing’ module.
The User agrees to refrain from:
- Posting any content that is illegal, prejudicial, insulting, racist, inciteful to hatred, revisionist, contrary to public decency, that infringes on privacy or on the privacy rights of third parties, in particular the publicity rights of persons and goods, intellectual property rights, or the right to privacy.
- Submitting content on behalf of a third party;
- Impersonate the identity of a third party and/or publish any personal information about a third party;
In general, the User undertakes to refrain from any unethical behaviour.
All Content (in particular text, comments, files, images, photos, videos, creative works, etc.), which may be subject to property or intellectual property rights, image or other private rights, shall remain the property of the User, subject to the limited rights granted by the terms of the licence granted by Promesse de fleurs as stated below. Users are at liberty to publish or not to publish such Content on the Site, notably via the ‘Photo Sharing’ facility, and accept that this Content shall be made public and freely accessible, notably on the Internet.
Users further acknowledge, undertake to have ,and guarantee that they hold all necessary rights and permissions to publish such material on the Site, in particular with regard to the legislation in force pertaining to any privacy, property, intellectual property, image, or contractual rights, or rights of any other nature. By publishing such Content on the Site, Users acknowledge accepting full liability as publishers of the Content within the meaning of the law, and grant Promesse de fleurs, free of charge, an inclusive, worldwide licence for the said Content for the entire duration of its publication, including all reproduction, representation, up/downloading, displaying, performing, transmission, and storage rights.
Users also grant permission for their name to be linked to the Content and accept that this link may not always be made available.
By engaging in posting material, Users consent to their Content becoming automatically accessible on the Internet, in particular on other sites and/or blogs and/or web pages of the Promesse de fleurs site, including in particular social pages and the Promesse de fleurs catalogue.
Users may secure the removal of entrusted content free of charge by issuing a simple request via our contact form.
The flowering period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, etc.)
It will vary according to where you live:
- In zones 9 to 10 (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), flowering will occur about 2 to 4 weeks earlier.
- In zones 6 to 7 (Germany, Poland, Slovenia, and lower mountainous regions), flowering will be delayed by 2 to 3 weeks.
- In zone 5 (Central Europe, Scandinavia), blooming will be delayed by 3 to 5 weeks.
In temperate climates, pruning of spring-flowering shrubs (forsythia, spireas, etc.) should be done just after flowering.
Pruning of summer-flowering shrubs (Indian Lilac, Perovskia, etc.) can be done in winter or spring.
In cold regions as well as with frost-sensitive plants, avoid pruning too early when severe frosts may still occur.
The planting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, United Kingdom, Ireland, Netherlands).
It will vary according to where you live:
- In Mediterranean zones (Marseille, Madrid, Milan, etc.), autumn and winter are the best planting periods.
- In continental zones (Strasbourg, Munich, Vienna, etc.), delay planting by 2 to 3 weeks in spring and bring it forward by 2 to 4 weeks in autumn.
- In mountainous regions (the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, etc.), it is best to plant in late spring (May-June) or late summer (August-September).
The harvesting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions in USDA zone 8 (France, England, Ireland, the Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...) fruit and vegetable harvests are likely to be delayed by 3-4 weeks.
In warmer areas (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), harvesting will probably take place earlier, depending on weather conditions.
The sowing periods indicated on our website apply to countries and regions within USDA Zone 8 (France, UK, Ireland, Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...), delay any outdoor sowing by 3-4 weeks, or sow under glass.
In warmer climes (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), bring outdoor sowing forward by a few weeks.















































