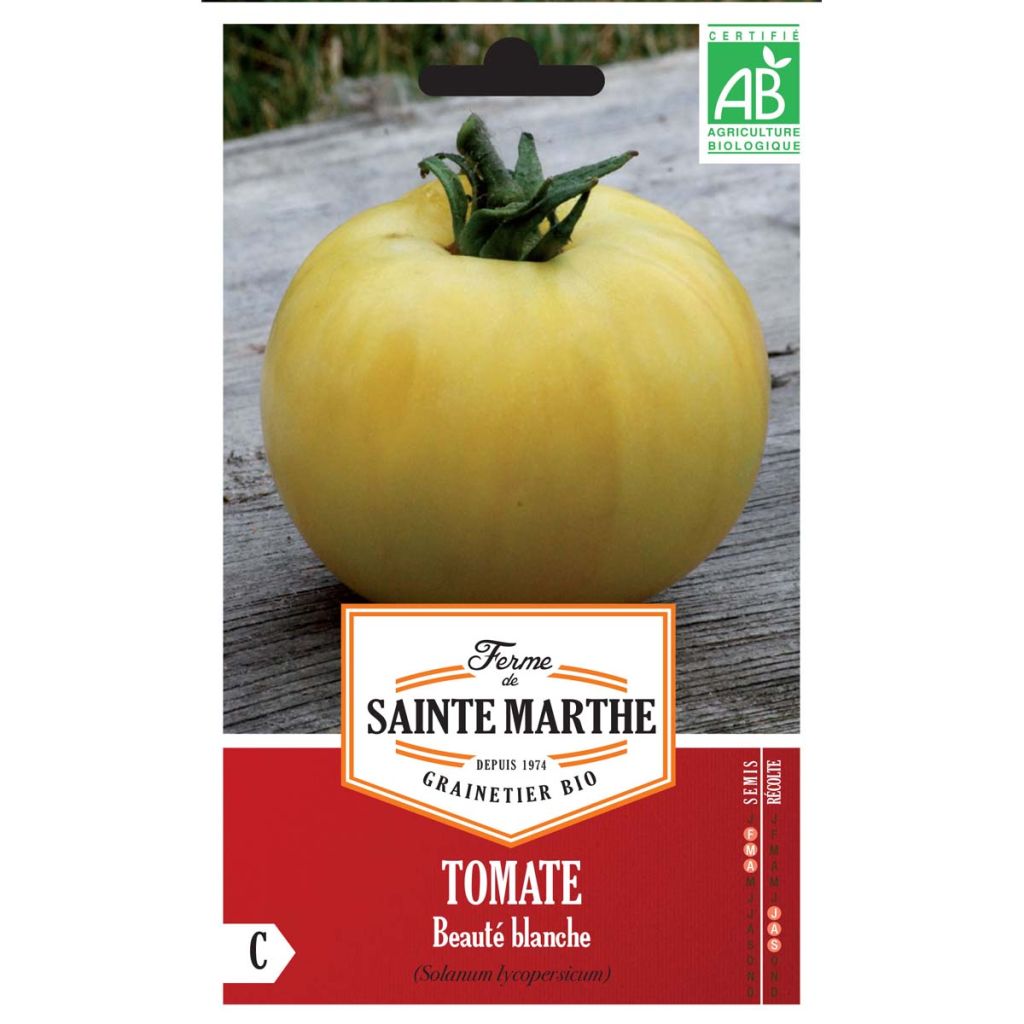


Tomato White Beauty - Ferme de Sainte Marthe seeds


Tomato White Beauty - Ferme de Sainte Marthe seeds
Tomato White Beauty - Ferme de Sainte Marthe seeds
Solanum lycopersicum Beauté Blanche
Tomato
This item cannot be shipped to the selected country
Dispatch by letter from €3.90
More information
Schedule delivery date,
and select date in basket
This plant carries a 6 months recovery warranty
More information
We guarantee the quality of our plants for a full growing cycle, and will replace at our expense any plant that fails to recover under normal climatic and planting conditions.
Seed-only orders are dispatched by sealed envelope. The delivery charge for seed-only orders is €3.90.

Description
The White Beauty Tomato is an early and productive variety, which produces round, pale yellow fruits weighing 100 to 75 g on vigorous plants. Their sweet and juicy flesh is of excellent quality, making them ideal for salads. Sow in March - April for a harvest from July to September.
The tomato is native to South America and Central America. Several varieties were already cultivated by the Incas long before the arrival of the Conquistadors. We are still amazed by the variety of this solanaceous plant. The term 'tomate' comes from the Incas' Tomatl and refers to both the plant and the fruit it produces. There are fruits of every colour, except perhaps blue, of all shapes and sizes. Ancient varieties are indeterminate plants and can live for two years. More recent varieties have a determinate growth and stop growing at the bush stage, so there is no need to stake or trellis them.
The tomato is one of the many foods that came to us from the New World, like beans, corn, squash, potatoes, and chili peppers. It took longer to reach our taste buds. For a long time, it was cultivated for its aesthetic and medicinal qualities. It was thought to be toxic because of its resemblance to the fruit of the mandrake, another solanaceous plant. It only became a regular on our tables in the early 20th century.
The tomato plant is a perennial herbaceous plant in tropical climates, but it is grown as an annual in our latitudes. It lignifies over time and produces small, insignificant yellow flowers grouped in cymes that will turn into fruits.
It must be admitted that its fruit is very attractive and adds a pleasant colour to the vegetable garden. It also has many nutritional advantages. Low in calories like most vegetables, rich in water, it contains a very interesting molecule: lycopene, a powerful antioxidant. And the longer the tomato is cooked, the more lycopene becomes available. It is also rich in vitamin C, provitamin A, and trace elements.
Today, its taste and nutritional qualities are undeniable. For gardeners, tomatoes are among the essential vegetables of summer. They just need to consider how they want to use them to guide them among all the existing varieties. Are they for salads, sauces, consuming directly on the spot, or cooked? They will also consider when they want to harvest them. The answer will of course depend on the average summer sunshine in the region where their garden is located. Rest assured, the choice is vast, and there is a tomato for every situation! And while tomatoes need a lot of sun and heat, they don't necessarily require a lot of space. That's why you shouldn't hesitate to grow them in containers on your balcony, where you will prefer varieties with small fruits. Be careful, immature fruits, stems, and leaves contain solanine and should not be consumed.
Harvesting: depending on the varieties, from early to late, it can take 50 to 100 days between the transplanting date and the harvest. There is no foolproof trick to determine in advance when a tomato has reached its full ripeness. Harvesting will be done when, at a minimum, it is completely coloured as announced and when its texture, while remaining firm, shows a slight softening. For better preservation, make sure to pick the fruit with its peduncle.
Preservation: tomatoes do not keep as long as their water content is high. They can be kept well for a few days in the vegetable drawer of your refrigerator or spread out in the open air. To keep them longer, consider culinary methods such as tomato confit, dried tomatoes, sauces, frozen fruits, canned tomatoes, jams, or juice. We love to confit them because it's so simple and delicious: cut your tomatoes in half and collect the juice. Place your half tomatoes face up on the baking sheet of your oven. Season with salt, pepper, and sugar, then bake at a very low temperature for at least one hour. Remove your tomatoes and consume immediately, or store them in a glass jar and cover with olive oil.
Gardener's tip: it is recommended to grow several varieties of tomatoes each year to minimize the risk of a complete loss of harvest due to climate or specific diseases. To counter the phenomenon of 'blossom end rot' - not a disease but a calcium deficiency - spray a comfrey maceration rich in calcium on your plants. When transplanting, do not hesitate to bury the stem up to the first leaves. This will stimulate the root system and ensure a bountiful fruit harvest. Winning combinations in the garden are often the same on the plate. It's a good mnemonic to remember that tomatoes and basil go well together.
Report an error about the product description
Harvest
Plant habit
Foliage
Botanical data
Solanum
lycopersicum
Beauté Blanche
Solanaceae
Tomato
South America
Annual
Other Tomato seeds
Planting and care
Soil preparation: Tomato plants are extremely easy to grow. Sunlight and warmth play a crucial role in the success of this cultivation. However, they can tolerate any type of soil, although they prefer rich and well-draining soil. If the soil is too compact, you can add a little sand to improve its structure.
Seed sowing in a greenhouse: From mid-February to May, sow your seeds indoors or in heated greenhouses using trays at around 20°C (68°F). Bury the seeds about 5 to 7 mm (0in) deep in special seed compost, as they need darkness to germinate. Avoid using compost at this stage, as it may burn the future roots. Tomato plants grow very quickly, with seeds usually germinating within two weeks on average. Do not discard a tray if the seeds have not germinated within this time period, as some varieties may take longer. Once the plants have reached a height of about 15 cm (6in), consider transplanting them.
Transplanting in open ground: Once the risk of frost has passed, usually after the "Ice Saints" in mid-May, transplant your seedlings into open ground. Choose the sunniest and warmest spots in your garden. Planting them at the base of a south-facing wall is an ideal position. Loosen the soil and dig a hole that is at least 3 to 4 times the volume of the plant's root system. Add some well-decomposed compost at the bottom. Place your plant in the hole, burying it up to the first set of leaves, and then backfill. Firm the soil, create a small basin around the base, and water generously. Be careful not to wet the leaves to protect your plants from fungal diseases.
Maintenance: Applying a layer of mulch around the base of your plants helps retain moisture and reduces the need for weeding. Tomato plants do not require excessive watering, as their root system can reach deep into the soil for available resources. Water thoroughly only during prolonged periods of drought.
Seedlings
Care
Intended location
-
, onOrder confirmed
Reply from on Promesse de fleurs
Vegetable seeds
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Hardiness is the lowest winter temperature a plant can endure without suffering serious damage or even dying. However, hardiness is affected by location (a sheltered area, such as a patio), protection (winter cover) and soil type (hardiness is improved by well-drained soil).
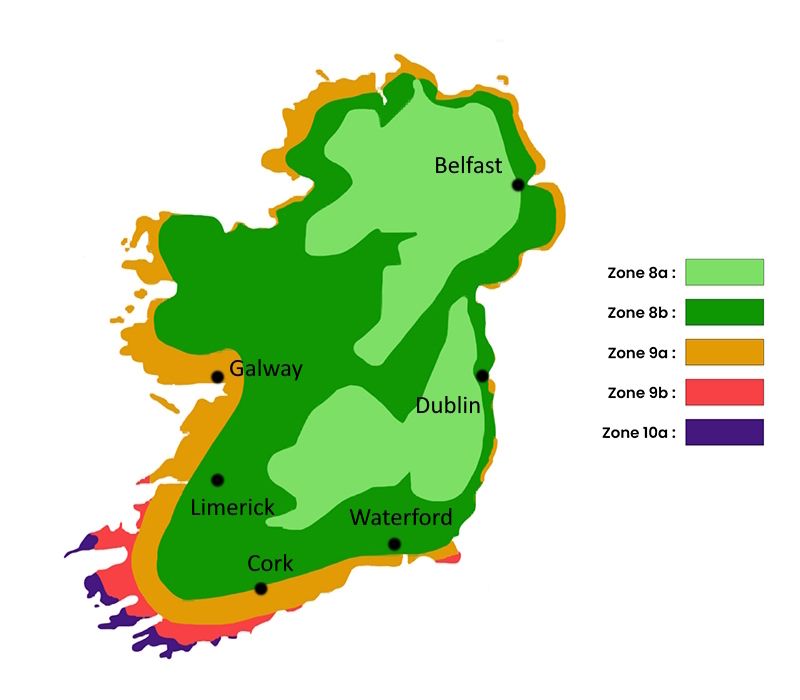
Photo Sharing Terms & Conditions
In order to encourage gardeners to interact and share their experiences, Promesse de fleurs offers various media enabling content to be uploaded onto its Site - in particular via the ‘Photo sharing’ module.
The User agrees to refrain from:
- Posting any content that is illegal, prejudicial, insulting, racist, inciteful to hatred, revisionist, contrary to public decency, that infringes on privacy or on the privacy rights of third parties, in particular the publicity rights of persons and goods, intellectual property rights, or the right to privacy.
- Submitting content on behalf of a third party;
- Impersonate the identity of a third party and/or publish any personal information about a third party;
In general, the User undertakes to refrain from any unethical behaviour.
All Content (in particular text, comments, files, images, photos, videos, creative works, etc.), which may be subject to property or intellectual property rights, image or other private rights, shall remain the property of the User, subject to the limited rights granted by the terms of the licence granted by Promesse de fleurs as stated below. Users are at liberty to publish or not to publish such Content on the Site, notably via the ‘Photo Sharing’ facility, and accept that this Content shall be made public and freely accessible, notably on the Internet.
Users further acknowledge, undertake to have ,and guarantee that they hold all necessary rights and permissions to publish such material on the Site, in particular with regard to the legislation in force pertaining to any privacy, property, intellectual property, image, or contractual rights, or rights of any other nature. By publishing such Content on the Site, Users acknowledge accepting full liability as publishers of the Content within the meaning of the law, and grant Promesse de fleurs, free of charge, an inclusive, worldwide licence for the said Content for the entire duration of its publication, including all reproduction, representation, up/downloading, displaying, performing, transmission, and storage rights.
Users also grant permission for their name to be linked to the Content and accept that this link may not always be made available.
By engaging in posting material, Users consent to their Content becoming automatically accessible on the Internet, in particular on other sites and/or blogs and/or web pages of the Promesse de fleurs site, including in particular social pages and the Promesse de fleurs catalogue.
Users may secure the removal of entrusted content free of charge by issuing a simple request via our contact form.
The flowering period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, etc.)
It will vary according to where you live:
- In zones 9 to 10 (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), flowering will occur about 2 to 4 weeks earlier.
- In zones 6 to 7 (Germany, Poland, Slovenia, and lower mountainous regions), flowering will be delayed by 2 to 3 weeks.
- In zone 5 (Central Europe, Scandinavia), blooming will be delayed by 3 to 5 weeks.
In temperate climates, pruning of spring-flowering shrubs (forsythia, spireas, etc.) should be done just after flowering.
Pruning of summer-flowering shrubs (Indian Lilac, Perovskia, etc.) can be done in winter or spring.
In cold regions as well as with frost-sensitive plants, avoid pruning too early when severe frosts may still occur.
The planting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, United Kingdom, Ireland, Netherlands).
It will vary according to where you live:
- In Mediterranean zones (Marseille, Madrid, Milan, etc.), autumn and winter are the best planting periods.
- In continental zones (Strasbourg, Munich, Vienna, etc.), delay planting by 2 to 3 weeks in spring and bring it forward by 2 to 4 weeks in autumn.
- In mountainous regions (the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, etc.), it is best to plant in late spring (May-June) or late summer (August-September).
The harvesting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions in USDA zone 8 (France, England, Ireland, the Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...) fruit and vegetable harvests are likely to be delayed by 3-4 weeks.
In warmer areas (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), harvesting will probably take place earlier, depending on weather conditions.
The sowing periods indicated on our website apply to countries and regions within USDA Zone 8 (France, UK, Ireland, Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...), delay any outdoor sowing by 3-4 weeks, or sow under glass.
In warmer climes (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), bring outdoor sowing forward by a few weeks.

























































